 |
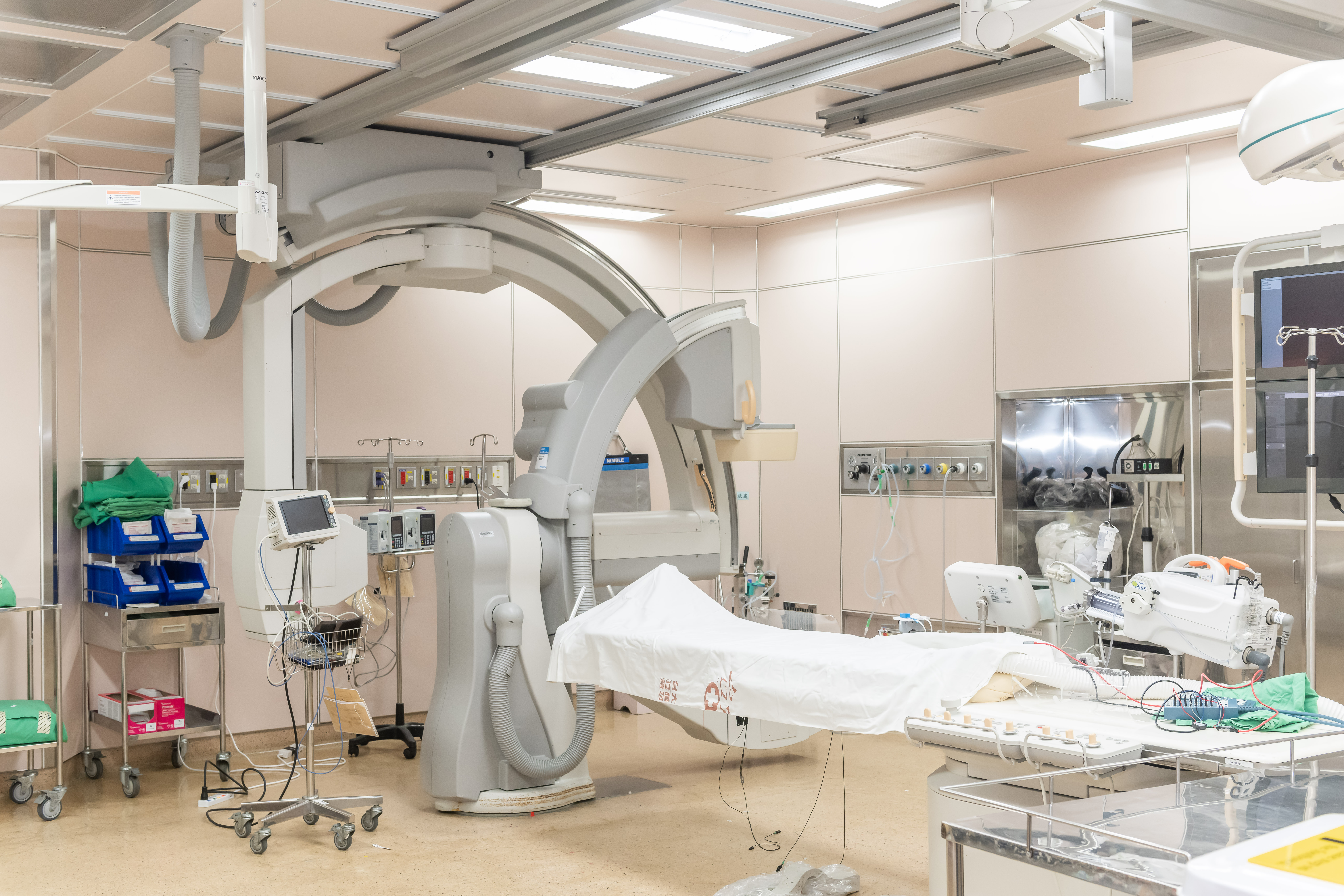 |
Cardiac catheterization is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube (catheter) is guided through a blood vessel to the heart to diagnose or treat certain heart conditions, such as clogged arteries or irregular heartbeats. Cardiac catheterization gives doctors important information about the heart muscle, heart valves and blood vessels in the heart. During cardiac catheterization, doctors can do different heart tests, deliver treatments, or remove a piece of heart tissue for examination. Some heart disease treatments — such as coronary angioplasty and coronary stenting — are done using cardiac catheterization. Usually, you'll be awake during cardiac catheterization but be given medications to help you relax. Recovery time for a cardiac catheterization is quick, and there's a low risk of complications.
Cardiac catheterization is a common procedure done to diagnose or treat a variety of heart problems. For example, your doctor may recommend this procedure if you have irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), chest pain (angina) or heart valve problems, among other things.
Cardiac catherization may be done at the same time as other heart procedures, such as:
1. Widening a narrowed artery (angioplasty) with or without stent placement
2. Closing holes in the heart and repairing other congenital heart defects
3. Replacing heart valves (heart valve surgery. e.g. TAVR)
4. Opening narrowed heart valves (balloon valvuloplasty)
5. Treating irregular heart rhythms with cold or heat energy (cardiac ablation)
6. Closing part of left atrium to avoid clot formation
7. Ablating heart muscle to relief heart pressure